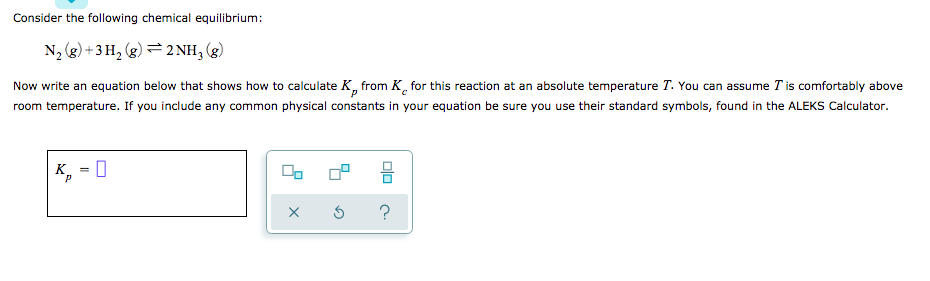
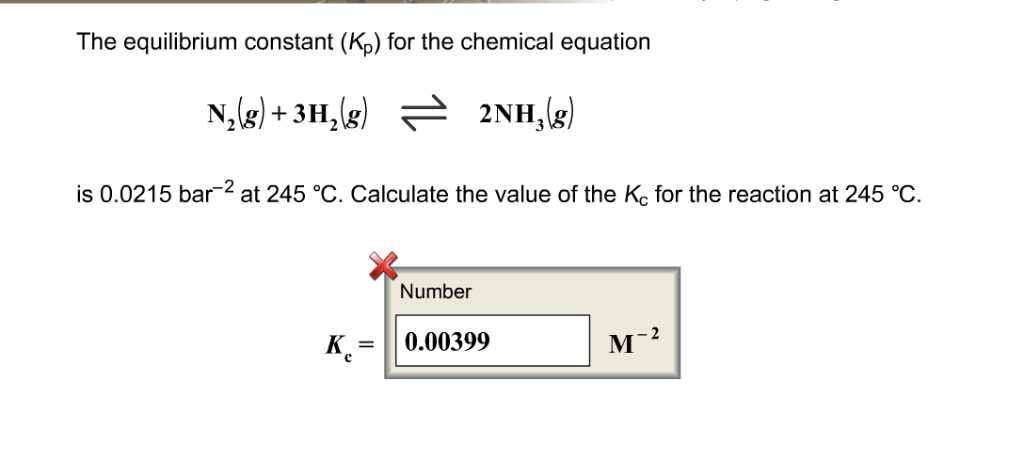
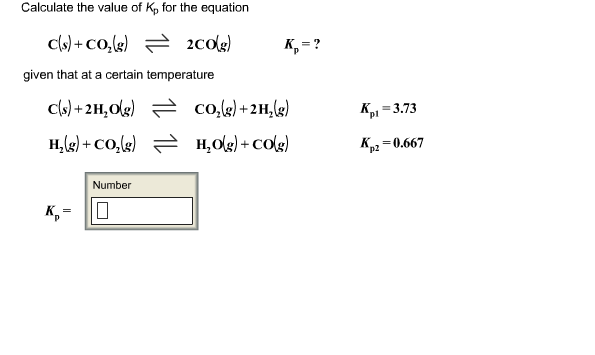
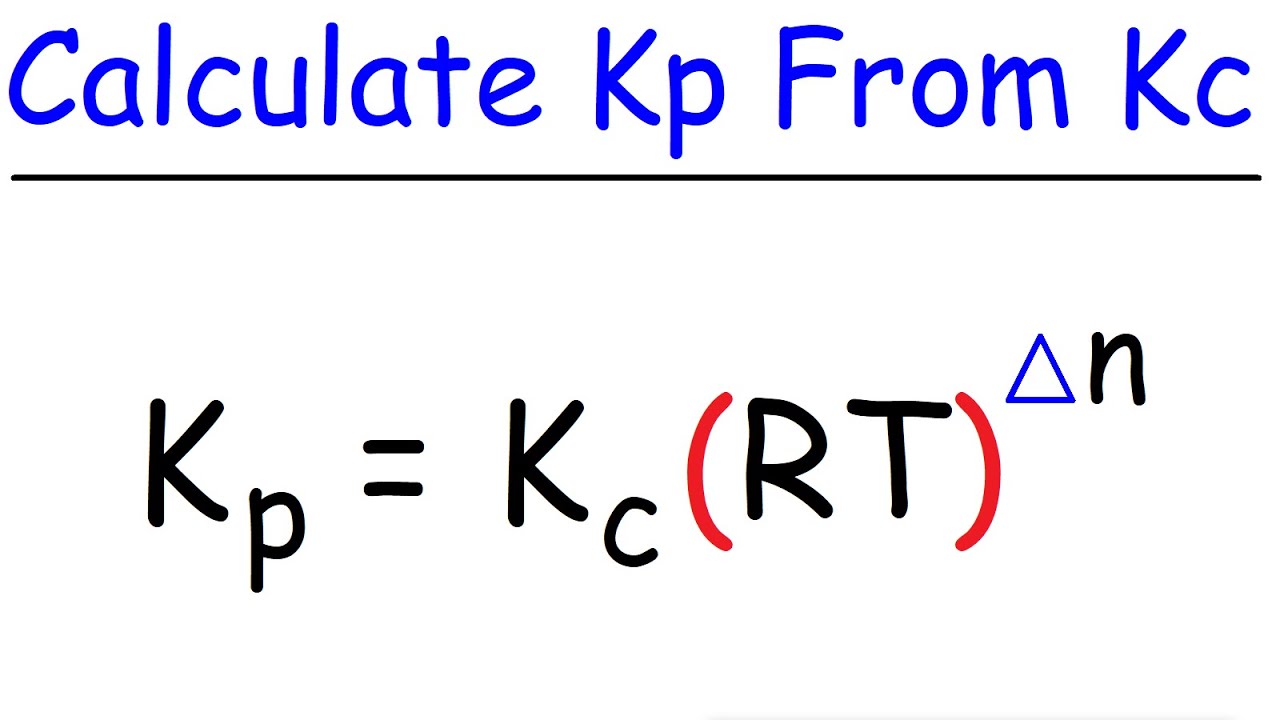
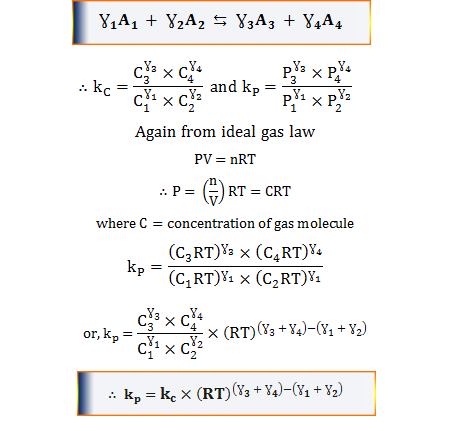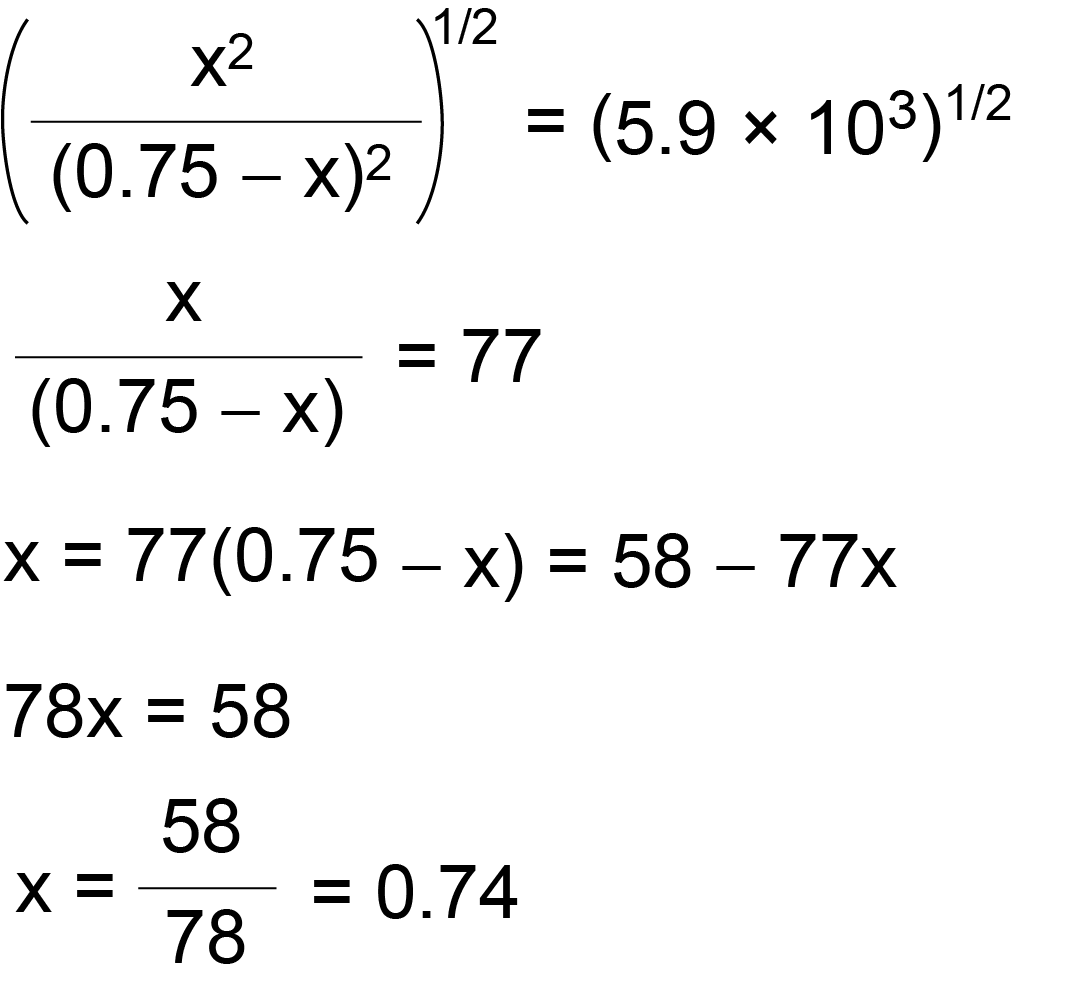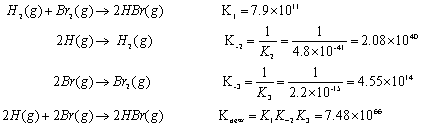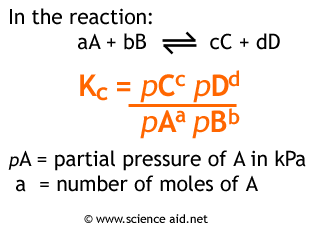OneClass: O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM interconverting Kp and Kc 一 Consider the following chemical eq...

SOLVED: Calculate Kc for each reaction. a. I2(g)x1e2 I(g) Kp = 6.26 * 10-22 (at 298 K) b. CH4(g) + H2O(g)x1eCO(g) + 3 H2(g) c. I2(g) + CI2(g)x1e2 IC1(g) Kp = 81.9 (
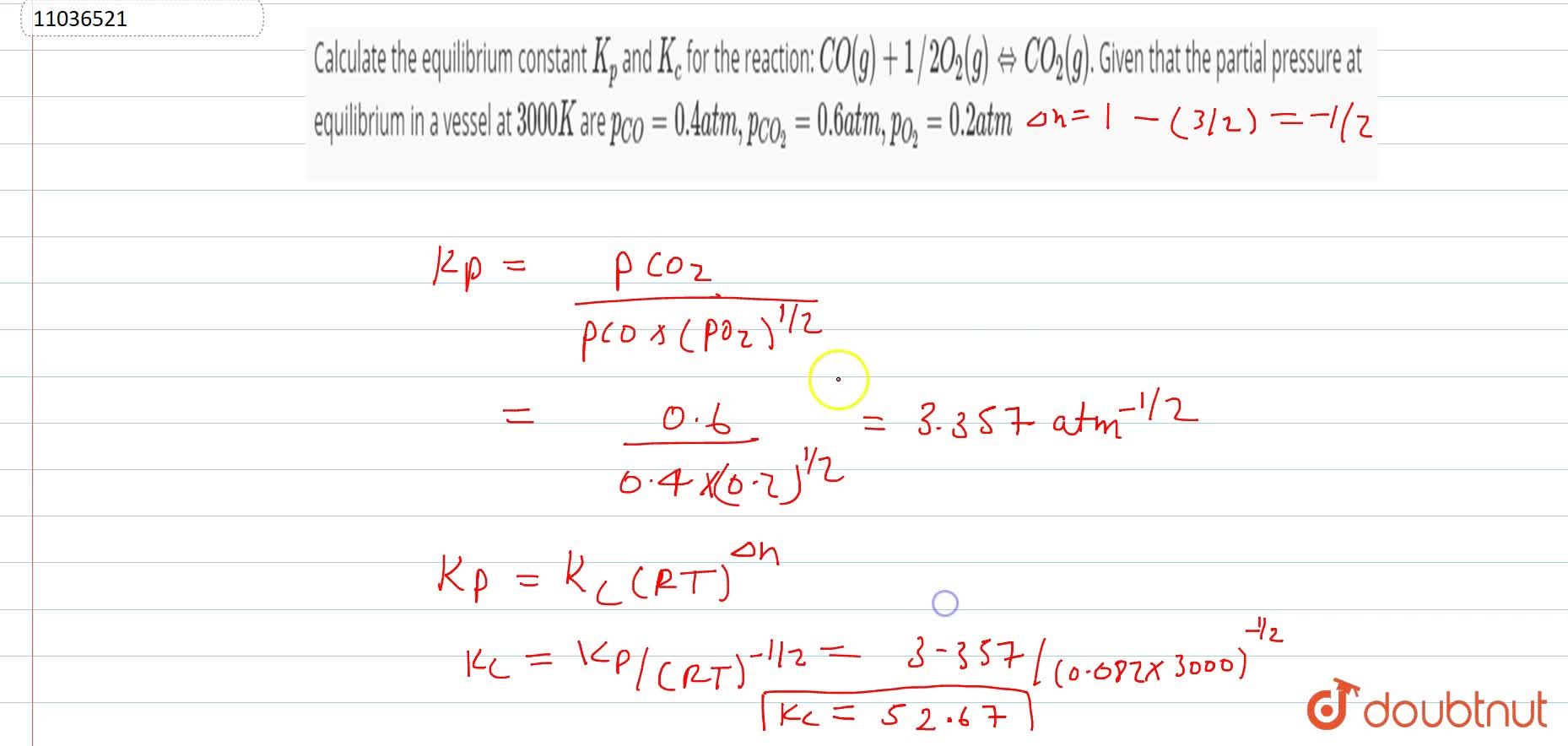
Calculate the equilibrium constant K(p) and K(c ) for the reaction: CO(g)+1//2O(2)(g) hArr CO(2)(g). Given that the partial pressure at equilibrium in a vessel at 3000 K are p(CO)=0.4 atm, p(CO(2))=0.2 atm

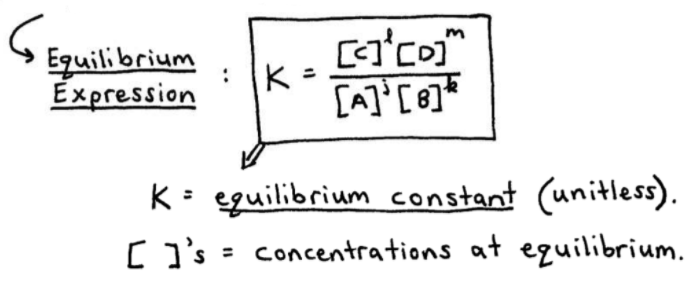
Chapter 15. Overview Equilibrium Reactions Equilibrium Constants K c & K p Equilibrium Expression product/reactant Reaction Quotient Q Calculations Le. - ppt download

SOLVED:The reaction CO2(g) + C(s) 2 CO(g) has Kp = 5.78 at 1200 K. a. Calculate the total pressure at equilibrium when 4.45 g of CO2 is introduced into a 10.0-L container